We Are AgrarIA Partners, an Artificial Intelligence Consortium Aimed at Boosting the Digitization and Sustainability of the Spanish Agri-food Sector.
Kimitec joins FLORETTE, HISPATEC, PRIMAFRIO, FAMILIA TORRES, SYLENTIS, and the CSIC as members of AgrarIA, the Artificial Intelligence (AI) consortium led by GMV within the Spanish agri-food value chain.
We are a consortium of twenty-four public-private entities driving this strategic collaboration with the purpose of evaluating AI as the fundamental technology to significantly transform the value chain of the Spanish agri-food sector, with IBM as a technological partner.
Define new agricultural production methods that will result in a more technological, innovative, and sustainable Spanish agri-food sector committed to energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction.
This is the main objective of the newly formed AgrarIA, a consortium of 24 organizations comprised of large corporations, SMEs, and research institutions with the common goal of increasing the competitiveness of the Spanish agri-food sector through R&D and the intensive use of AI and other Digital Enabling Technologies.
What is our role in the AgrarIA project?
To provide a natural alternative to the agri-food sector capable of responding to the fundamental changes in agriculture brought about by the Green Deal and its Farm to Fork strategy, while also meeting the Zero Residue standards of the broad distribution chain.
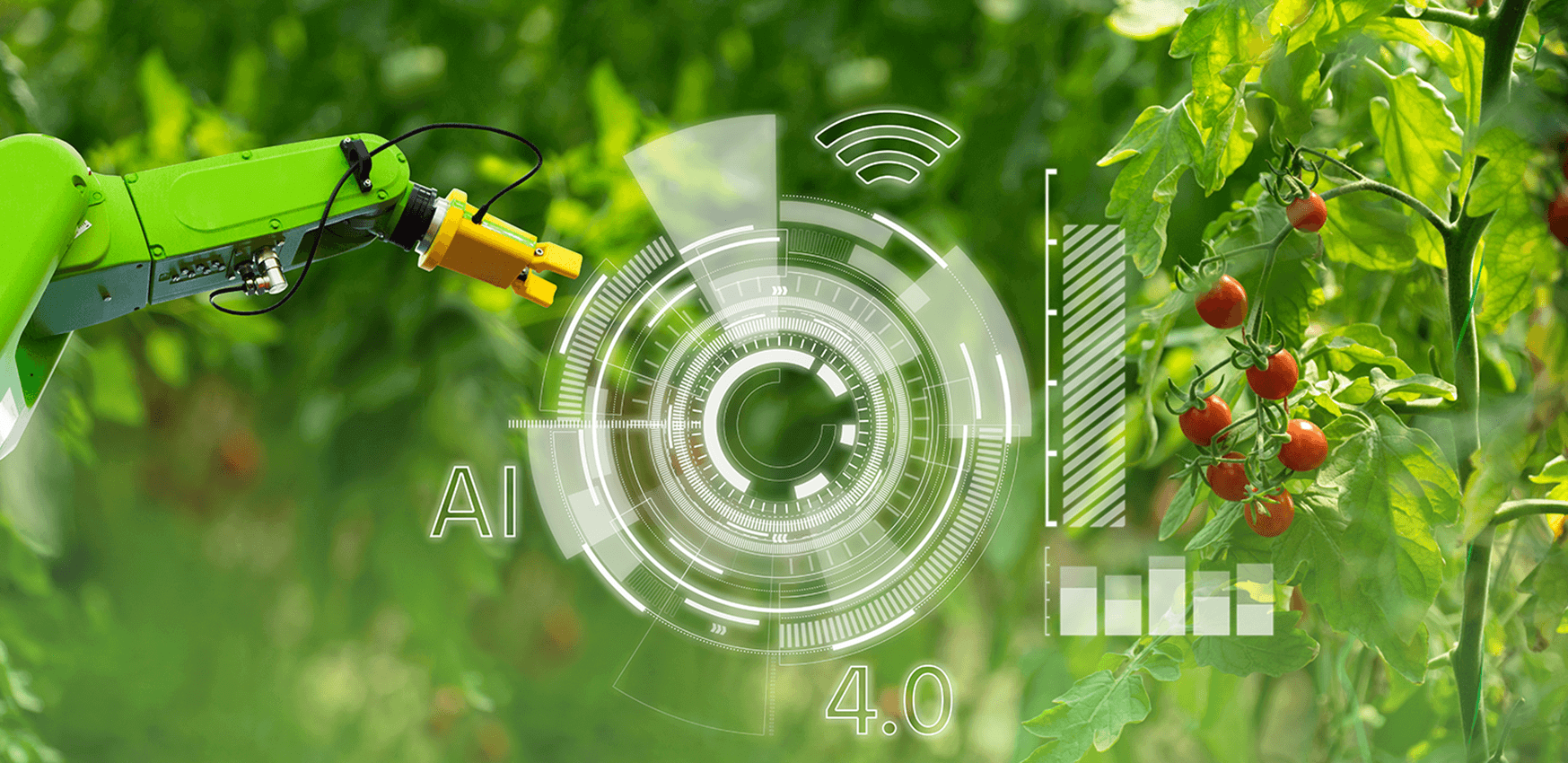
Using groundbreaking technology, such as artificial intelligence, as part of the process to develop novel biocontrol solutions of equal or higher efficacy than conventional synthetic pesticides. In this project, we will focus on the application of artificial intelligence (AI) for the biocontrol of greenhouse tomato pests.
To that end, we will investigate the development of processes to predict the biological action of a specific molecule and compound when it acts on pathogenic organisms that affect tomato, as well as understanding the molecular mechanisms that determine its biopesticidal action via analytical and Machine Learning methodologies, which will allow us to acquire phenotypic and transcriptomic data from fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases.
The tomato “CV. Micro-Tom” will be used as the project’s model species since it has been thoroughly documented and a considerable amount of data on its genomic and genetic material is available in public sources, facilitating the study of genetic regulatory networks.
AI applied to the agri-food production value chain
AgrarIA is envisioned as a decoupled and standards-based platform that will enable the development and integration of agri-food value chain models and support elements, as well as the workflows of Artificial Intelligence processes based on horizontal technologies required for the implementation of unique initiatives or specific use cases applied to the agri-food sector.
The platform will enable collaboration among public-private organizations from various industries to address the most significant challenges in the Spanish agri-food sector, using AI and developing a framework of development and collaboration with the mutual interest of using AI to optimize the products and services they offer to the market.
Regarding the Spanish agri-food sector
The Spanish agri-food sector significantly contributes to our country’s productive wealth. With over 50,000 million euros in exports and a workforce of approximately 2.6 million people, the sector is a key driver of growth. It is comprises over 900,000 farms and over 31,000 food companies, with small and medium-sized businesses accounting for 95 % of the business fabric and 80 % of the organizations employing fewer than ten people.
Looking to the future, the Spanish agri-food sector faces several challenges, the most significant of which is increasing its level of digitalization. This digital potential is being explored in tandem with agriculture 4.0, which is centered on IoT, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, and other digital enabling technologies with the objective of transforming the production capacity of the entire supply value chain.
In this context, the AgrarIA platform will support the transition to a carbon-neutral global industry by 2050 by employing AI, robotics, and biotechnology to identify breakthrough agricultural production methods.
This project is financed by the Secretary of State for Digitization and Artificial Intelligence (SEDIA) of the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Digital Transformation’s Artificial Intelligence R&D Missions Program, as part of the Recovery, Transformation, and Resilience Plan.
The companies participating in the project are:
1A ENGINEERS, SLP; STATE AGENCY SUPERIOR COUNCIL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH; AGERPIX; AMETLLER HOUSE; Celtiberian Solutions SL; CODESIAN SOFTWARE TECH SL; DRONETOOLS, SL; EMERGYA ENGINEERING SL; FLORETTE IBÉRICA, SL; GMV; HISPATEC GROUP INFORMÁTICA EMPRESARIAL SA; TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF CASTILLA Y LEÓN (ITCL); Intelligence Solagua, SL; KIMITEC; KIVNON LOGISTICS SL; DIGITAL SHUTTLE SL; LB-BAGGING, SL; MIGUEL TORRES, SA; PRIMAFRIO SL; Secmotic Innovation SL; Sylentis SA, sole proprietorship; TEPRO Agricultural Consultants SL; University of Salamanca; Sevilla University.
